Lupus, An Irreversible Disease without Cure

“God is our refuge and strength, a very present help in trouble. Therefore will not we fear, though the earth be removed, and though the mountains be carried into the midst of the sea; though the waters thereof roar and be troubled, though the mountains shake with the swelling thereof. Selah.”
Psalm 46:1-3
Lupus, An Irreversible Disease without Cure
BY. MELINE NGO
Lupus, a chronic autoimmune disease, affects millions of individuals worldwide. This disease not only poses significant health challenges but also lacks a definitive cure. Lupus can cause severe damage to various organs, leading to a reduced quality of life and increased mortality rates. Understanding the nature of this irreversible disease becomes crucial in comprehending the impact it has on its sufferers and the urgent need for improved treatments.

- Definition and Types of Lupus:
Lupus, scientifically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a complex autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues and organs. There are several types of lupus, including discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE), neonatal lupus, and drug-induced lupus erythematosus (DILE). However, SLE is the most common and severe form of the disease.
- Symptoms and Complications:
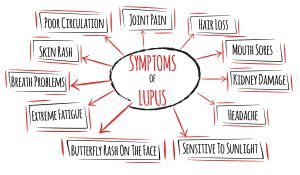
The symptoms of lupus can vary from person to person, making it a challenging ailment to diagnose. Common manifestations include fatigue, joint and muscle pain, skin rashes, fever, hair loss, kidney problems, cardiovascular complications, and neurological disorders. These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s daily life, making even the simplest tasks difficult to carry out.
- Disease Progression and Organ Damage:
Lupus is characterized by periods of remission and flares. During flares, the disease can become more aggressive, leading to increased inflammation and damage to various organs. Organs commonly affected by lupus include the kidneys, heart, lungs, brain, skin, and joints. Over time, this progressive damage can become irreversible, further worsening the patient’s prognosis.
- Treatment Options and Challenges:
Although there is no known cure for lupus, healthcare professionals aim to alleviate symptoms, prevent flares, and manage organ damage to improve the patient’s quality of life. Treatment plans typically involve a combination of medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologics. However, finding the right combination and dosage can be a complex and ongoing process due to individual variability and potential side effects associated with these medications.
- Addressing the Need for Research and Awareness:
Given the lack of a cure for lupus, continued investments in research are paramount. Scientists and specialists are working tirelessly to uncover the root causes of lupus, develop targeted therapies, and find ways to modulate the immune system’s response. Increased awareness of the disease within the general population can help foster support, promote fundraising, and drive research forward.
Lupus, an irreversible disease without a cure, poses significant challenges for those affected. With its diverse range of symptoms, potential organ damage, and lifelong management requirements, it is crucial to acknowledge and support individuals battling this chronic condition. Advancements in research and awareness will play an integral role in improving treatments, enhancing patient outcomes, and ultimately striving toward finding a cure for this debilitating autoimmune disease.

 Copyright secured by Digiprove © 2023 meline Ngo
Copyright secured by Digiprove © 2023 meline Ngo

Recent Comments